SPLINE Command

Using the SPLINE Command for the Construction Path in Solid Modeling Tools will result it to break into segments.
Creates a smooth curve that passes through or near a set of fit points, or that is defined by the vertices in a control frame.
SPLINE creates curves called nonuniform rational B-splines (NURBS), referred to as splines for simplicity.
Splines are defined either with fit points, or with control vertices. By default, fit points coincide with the spline, while control vertices define a control frame. Control frames provides a convenient method to shape the spline. Each method has its advantages.
To display or hide the control vertices and control frame, select or deselect the spline, or use CVSHOW and CVHIDE. However, for splines created with control vertices in AutoCAD LT, you can display the control frame only by selecting the spline.
The prompts differ, depending on whether you choose Fit or CV (Control Vertices) as the creation method (Method option).
First Point
Specifies the first point of the spline, either the first fit point or the first control vertex, depending on the current method.Next PointCreates additional spline segments until you press Enter.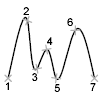 UndoRemoves the last specified point.CloseCloses the spline by defining the last point to be coincident with the first. By default, closed splines are periodic, maintaining curvature continuity (C2) along the entire loop.
UndoRemoves the last specified point.CloseCloses the spline by defining the last point to be coincident with the first. By default, closed splines are periodic, maintaining curvature continuity (C2) along the entire loop.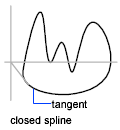
Method
Controls whether the spline is created with fit points or with control vertices. (SPLMETHOD system variable).FitCreates a degree 3 (cubic) B-spline by specifying fit points that the spline must pass through. When the tolerance value is greater than 0, the spline must pass through. When the tolerance value is greater than 0, the spline must be within the specified tolerance distance from each point.Control Vertices (CV)Creates a spline by specifying control vertices. Use this method to create splines of degree 1 (linear), degree 2 (quadratic), degree 3 (cubic), and so on up to degree 10. Adjusting the shape of a spline by moving control vertices often provides better results than moving fit points.
Object
Converts 2D or 3D quadratic or cubic spline-fit polylines to equivalent splines. The original polyline is retained or discarded depending on the setting of the DELOBJ system variable.
Prompts for Splines with Fit Points
The following prompts are specific to the fit point method:
KnotsSpecifies the knot parameterization, one of several computational methods that determines how the component curves between successive fit points within a spline are blended. (SPLKNOTS system variable).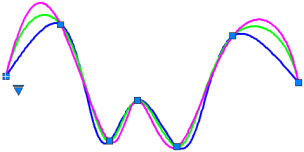
- Chord. (Chord-Length method) Spaces the knots connecting each component curve to be proportional to the distances between each associated pair of fit points. An example is the green curve in the illustration.
- Square Root. (Centripetal method) Spaces the knots connecting each component curve to be proportional to the square root of the distance between each associated pair of fit points. This method usually produces "gentler" curves.
- Uniform. (Equidistant method). Spaces the knows of each component curve to be equal, regardless of the spacing of the fit points. This method often produces curves that overshoot the fit points.
Start TangencySpecifies a tangent condition on the starting point of the spline.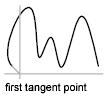 End TangencySpecifies a tangent condition on the ending point of the spline.
End TangencySpecifies a tangent condition on the ending point of the spline. ToleranceSpecifies the distance by which the spline is allowed to deviate from the specified fit points. A tolerance value of 0 requires the resulting spline to pass directly through the fit points. The tolerance value applies to all fit points except the starting and ending fit points, which always have a tolerance of 0.
ToleranceSpecifies the distance by which the spline is allowed to deviate from the specified fit points. A tolerance value of 0 requires the resulting spline to pass directly through the fit points. The tolerance value applies to all fit points except the starting and ending fit points, which always have a tolerance of 0.
Prompts for Splines with Controls Vertices
The following prompt is specific to the control vertices (CV) method. (SPLMETHOD system variable).
DegreeSets the polynomial degree of the resulting spline. Use this option to create splines of degree 1 (linear), degree 2 (quadratic), degree 3 (cubic), and so on up to degree 10.
Powered by AutoCAD®
Related Articles
REVOLVE Command
Creates a 3D solid or surface by sweeping an object around an axis. Open profiles create surfaces and closed profiles can create either a solid or a surface. The Mode option controls whether a solid or a surface is created. When creating a surface, ...BLEND Command
Creates a spline in the gap between two selected lines or curves. Select each object near an endpoint. The shape of the resulting spline depends on the specified continuity. The lengths of the selected objects remain unchanged. Valid objects ...JOIN Command
Joins the endpoints of linear and curved objects to create a single object. Combines a series of finite linear and open curved objects at their common endpoints to create a single 2D or 3D object. The type of object that results depends on the types ...DIVIDE Command
Creates evenly spaced point objects or blocks along the length or perimeter of an object. The following prompts are displayed: Select Objects to Divide Specifies a single geometric object such as a line, polyline, arc, circle, ellipse, or spline. ...REVSURF Command
Creates a mesh by revolving a profile about an axis. Select a line, arc, circle, or 2D or 3D polyline to sweep in a circular path around a selected axis. The MESHTYPE system variable sets which type of mesh is created. Mesh objects are created by ...
Recent Articles
Microvellum Foundation Library Release Notes | Build 26.0220
The following release notes apply to the Microvellum Foundation Library build 26.0220. Additions Added DTC Magic Pro and Magic Star Ultra drawer systems. Magic Pro Items added in hardware file 300 and 600 lengths for all drawer heights. Add 60kg ...Microvellum Release Notes | Build 25.2.0223.641
The following release notes apply to Microvellum build 25.2.0223.641. Add 2D Elevation Tokens to 3D Drawings Fig. 1: The new 2D Elevation setting. A popularly requested feature by the community has been added to the Microvellum software: the checkbox ...Microvellum Processing Center Application
The standalone Processing Center application provides shop-floor tools for managing and executing manufacturing data generated from Microvellum projects. It enables users to: Print part labels View and print reports Create and re-create manufacturing ...Microvellum Release Notes | Build 25.2.0213.641
The following release notes apply to Microvellum build 25.2.0213.641 File Name Fix An issue was occurring when processing work orders with the Create Sequential File Names setting enabled. When the setting was enabled, a work order being processed ...Microvellum Release Notes | Build 25.2.0206.641
The following release notes apply to Microvellum build 25.2.0206.641. Item Number Fix An issue was reported regarding item numbers in composite drawings. Users who processed work orders with multiple products reported that the item numbers would ...